Units & Measurement Notes – JEE Mains, Advanced, NEET & CBSE Class 11
1. Introduction
This chapter covers the fundamentals of measurement in physics: physical quantities, SI units, dimensional analysis, significant figures, errors, and key formulas — essential for JEE Mains, JEE Advanced, NEET & CBSE.
2. Physical Quantities & Units

- Fundamental Quantities: Length, Mass, Time, Electric Current, Temperature, Amount of Substance, Luminous Intensity
- Derived Quantities: Speed, Force, Pressure, etc.
- SI Units: Standard global units—learn more on Wikipedia
3. Systems of Units
| System | Length | Mass | Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| CGS | cm | g | s |
| FPS | ft | lb | s |
| MKS | m | kg | s |
| SI | m | kg | s |
4. Measurement Techniques
Length
Use vernier calipers and screw gauge for precision. Also utilize meter scale and parallax method for large-scale measurements.
Mass
Measured using beam or electronic balances.
Time
Measured via stopwatch, clocks, or atomic clocks (~10⁻¹³ s precision).
5. Significant Figures & Precision
Significant figures reflect measurement accuracy, while precision indicates consistency of repeated readings.
- All non-zero digits are counted
- Zeros between non-zero digits are significant
- Trailing zeros in decimal form are significant
Examples: 0.00456 → 3 sig‑figs; 500.0 → 4 sig‑figs.
6. Errors & Uncertainty
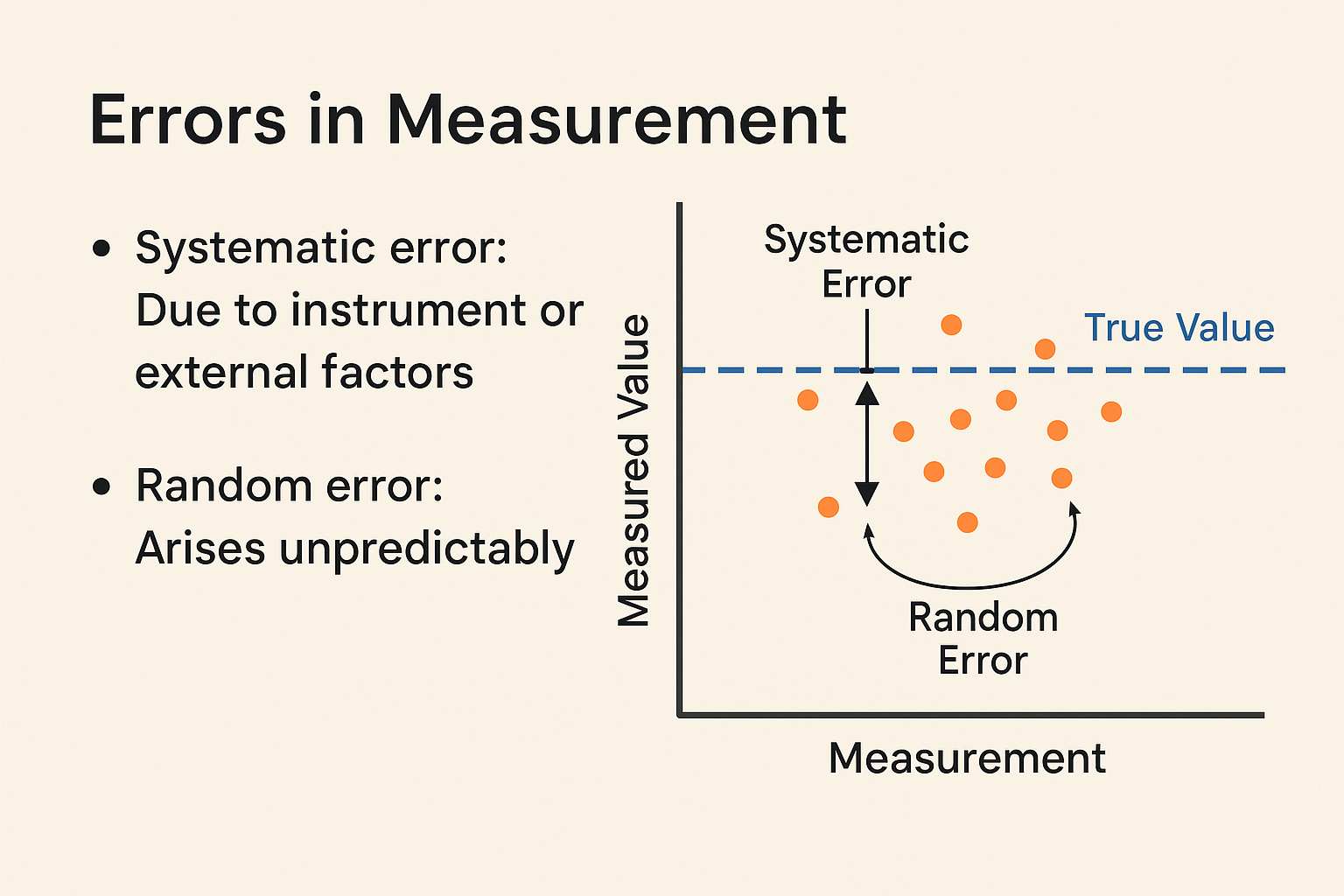
Types of Errors:
- Systematic: calibration or instrument bias
- Random: unpredictable variations
- Gross: human mistakes
Error Calculations:
- Absolute error: ΔA = |measured − true value|
- Relative error: ΔA ÷ true value
- Percentage error: (ΔA ÷ true value) × 100%

Propagation: add absolute errors in sums/differences, and relative errors in multiplication/division.
7. Dimensional Analysis

Dimensional formula expresses physical dimensions as [MaLbTc]. Example: Force = mass × acceleration → [M¹L¹T⁻²].
- Check equation validity
- Derive and confirm formulae
- Perform unit conversions
8. Formulae Summary
| Quantity | Dimensional Formula | SI Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Velocity | [M⁰L¹T⁻¹] | m/s |
| Acceleration | [M⁰L¹T⁻²] | m/s² |
| Force | [M¹L¹T⁻²] | newton (N) |
| Work/Energy | [M¹L²T⁻²] | joule (J) |
| Power | [M¹L²T⁻³] | watt (W) |
| Pressure | [M¹L⁻¹T⁻²] | pascal (Pa) |
9. Watch: Units & Measurement Explained
10. FAQs
Q: Why are SI units important?
A: They standardize measurements globally for accuracy and consistency.
Q: What is the principle of homogeneity?
A: Equations are valid only if both sides have identical dimensions.
Q: How do you combine errors in multiplication?
 A: Add the relative errors of each factor to get the final error.
A: Add the relative errors of each factor to get the final error.
Q: What is dimensional analysis and why is it important?
A: It’s a method used to check the validity of equations and convert units by analyzing the dimensions of physical quantities.
Q: How is the accuracy of Vernier Calipers and Screw Gauge different?
A: Vernier Calipers offer ~0.1 mm precision, while Screw Gauges provide higher precision (~0.01 mm), ideal for small object measurements.
Related Links 🔗
- JEE Main – Official Website
- JEE Advanced – Official Website
- NEET – Official Website
- CBSE – Official Website
- NCERT Physics Class 11
 JEE Prep Guide
JEE Prep Guide